Content
- Causes of eczema on the hands
- How to treat eczema on the hands at home
- Diet for eczema
- Features of the treatment of hand eczema
Nervous stress affects not only the internal state of the body. It can also appear externally – in the form of eczema of the skin. This chronic disorder gives a person pain and discomfort. The instructions below will help you figure out how to treat eczema on your hands. Such skin irritation can be treated with official and traditional medicine.
Causes of eczema on the hands
This chronic skin disease in the form of inflammation of the upper epidermis is not contagious. Eczema on the hands of the idiopathic form has been little studied, but doctors were able to identify a number of provoking factors:
- emotional overstrain, depression;
- endocrine system diseases;
- digestive system diseases;
- diabetes;
- vegetovascular dystonia;
- deficiency in the diet of vitamin B6, fatty acids;
- worm infection;
- kidney dysfunction;
- intestinal dysbiosis;
- low immunity.
How to treat eczema on the hands at home
In most cases, local treatment is performed. Antibiotics are added to the treatment of the microbial type of the disease, and allergic – limiting the person’s contact with the allergen, proper nutrition and bed rest. In addition to these 2 forms, other types of infection are isolated:
- idiopathic;
- atopic;
- professional;
- fungal and seborrheic;
- dyshidrotic.
Medicine
The doctor may prescribe medication for a particular form of the disease. Eczema on the hands on a nervous basis is treated with such drugs:
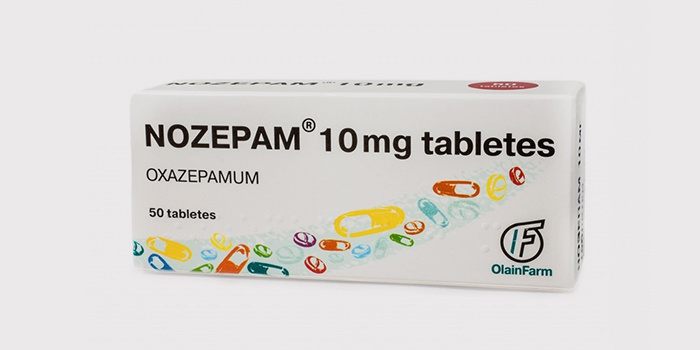
- Soothing – “Bromkamfora” 5 ml or “Sodium Bromide” 10 ml three times a day for 2 weeks.
- Tranquilizers – “Nozepam”, “Chlozepide”, “Phenozepam”.
- Herbal preparations – Novopassit, Persen, Peony Tincture.
Hormonal drugs are prescribed for severe manifestations of inflammation. It can be Dexamethasone, Corticotropin, Prednisolone. Mandatory for the treatment of the inflammatory process on the hands is vitamin therapy:
- vitamin E oil solution, injections of vitamin B;
- ordinary ascorbic;
- folic acid.
With any type of eczema, antihistamines are prescribed:
- For severe manifestations of inflammation – “Diphenhydramine”, “Promethazine”, “Chloropyramine.” They are introduced bypassing the gastrointestinal tract.
- Other anti-allergic medicines – Cetrin, Desal, Clarisens, Suprastin.
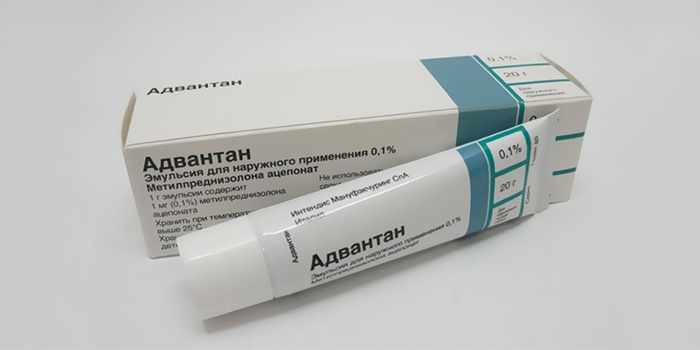
If a dependence of inflammation on gastrointestinal tract disorders is detected, then Pancreatin, Festal, Enzystal, Panzinorm Forte and probiotic Hilak Forte, Bifiform or Laktobakterin are prescribed. The microbial form involves treatment with antifungal drugs, such as Nystatin, Levorin, Pimafucin. Local therapy is an ointment for eczema on the hands. The most effective dermatologists consider the Advantan fatty remedy:
- lubricate affected skin surfaces once a day;
- this ointment for eczema on the fingers practically has no contraindications;
- the course of treatment continues until positive results are obtained, sometimes up to several months.
Cream
How to get rid of eczema on your hands forever? After treatment, numerous creams are used for prevention:
- “Elokom.” Indications are a fungal, viral, or bacterial infection. It is necessary to cover damaged areas once a day. The duration of treatment depends on the achievement of the effect of application.
- “Celestoderm.” An external medicine for eczema on the hands. It is necessary to cover the affected areas with a thin layer up to three times a day. The course of treatment until symptoms are resolved.
- “Elidel.” Anti-inflammatory cream for the treatment of the disease on the hands of an adult or a child if he is older than 3 months. It is necessary to smear the cream on the affected areas up to 2 times a day. Repeat procedures until symptoms are completely eliminated..
Folk remedies
Here’s how to treat eczema on your hands with folk remedies:
- Hand baths for eczema. This method is recommended for dry eczema. Dilute in 1 liter of hot water 2 tbsp. salt. When the liquid cools down a little, place your hands in the bath and do not reach until completely cooled. Repeat the method every day.
- Emulsion. To treat a wet form, break 1 chicken egg, add 50 ml of table vinegar. Dilute with the same amount of water. Stir until a homogeneous consistency, spread over the hands, wrap them with a soft cloth. In the morning, do not wash off the resulting film. In the evening, repeat the procedure again..
- Kalanchoe. The juice of this plant lubricate the lesion every day.
Diet for eczema
When treating eczema, you need to normalize your diet. Include dairy and vegetable products in your diet, and discard this:
- spicy, salty foods;
- strong meat broths;
- egg protein;
- fried meat;
- smoked meats;
- sweets;
- alcoholic drinks.
Features of the treatment of hand eczema
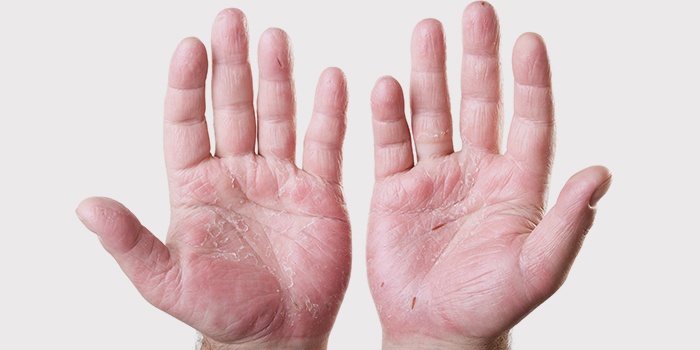
Eczema is also classified by the nature of the course of the disease. Here’s what eczema looks like on hand:
- Dry. Dryness and cracking of the skin of the hands are characterized. Exacerbates more often in winter, when air humidity is lowered. Leaking in chronic form.
- Soaking. It often appears on the hands and is a transformation of the dry form. As you can see in the photo, the characteristic signs are redness between the fingers and on the hands themselves, swelling and itching. Bubbles form, which then burst, releasing fluid, and cause the appearance of depressions in the epidermis.
Dry
It is important to know what measures are taken to treat dry eczema:
- Lubrication with corticosteroid ointments to eliminate peeling. Specifically, what to treat eczema on the hands in the initial stage, doctors will tell.
- Timely treatment, because dry eczema very quickly flows into the weeping.
- Regular softening with creams of the skin after treatment.
- Exclusion of a stress factor so that there are no relapses.
- Minimization of water procedures.
- Allergen Exclusion.
Wet
Weep-type eczema develops from a dry form and is associated with immune deficiency. Features of her treatment:
- Lack of decoration in damaged areas.
- Exclusion of cosmetics such as perfumes and deodorants.
- Change of ordinary powder and soap to nurseries where there are no fragrances and dyes.
- Compliance with the diet, the exclusion of citrus fruits and bright red berries.
- Reduced contact with water.
- The use of antibacterial and antifungal drugs, because weeping eczema often develops due to fungi of the genus Candida.