Content
- Why do clots come out during menstruation?
- Causes of Menstrual Clots
- In which cases it is worth visiting a doctor?
- Treatment
During menstruation, almost every woman has blood clots. They are often accompanied by prolonged and painful bleeding, but doctors believe that this is normal. However, when a woman has too strong clots during menstruation, this may be a sign of a gynecological disease, and how to distinguish a deviation from the norm, try to figure it out.
Why do clots come out during menstruation?
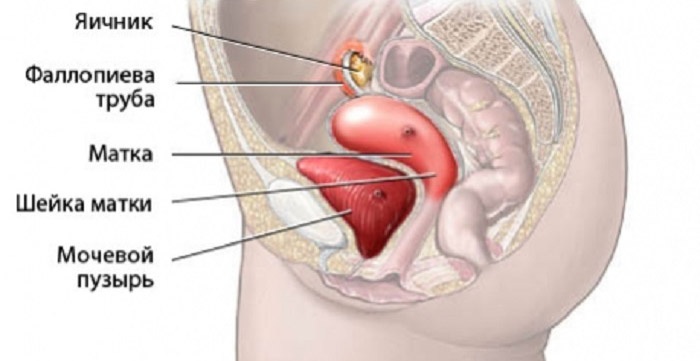
During the menstrual cycle, the walls of the uterus thicken, preparing for fertilization. If pregnancy does not occur before menstruation, the endometrial layer is rejected, which is accompanied by bleeding. During menstruation, the body loses up to 250 ml of blood, but if blood loss is a larger volume, then this is considered an excess of the norm. With strong secretions, blood clots form, which are essentially small blood clots.
Causes of Menstrual Clots
If a large number of large clots forms during menstruation, then this is an occasion for contacting a gynecologist. After examination, the doctor will identify their cause, because there may be several possible pathologies:
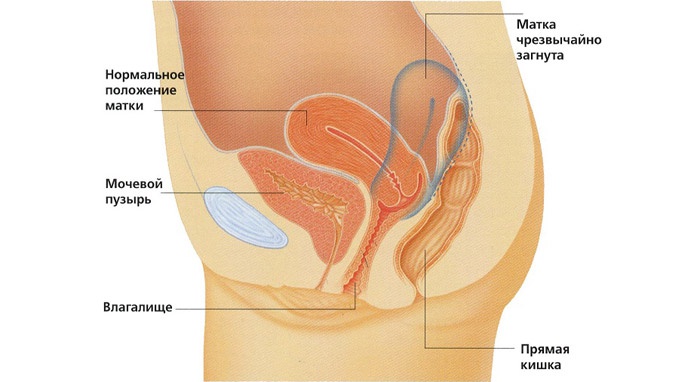
- bending of the uterus;
- blood clots
- uterine fibroids;
- endometriosis;
- diseases of the pelvic organs;
- an abnormality of the uterus;
- hormonal imbalance;
- bleeding disorder.
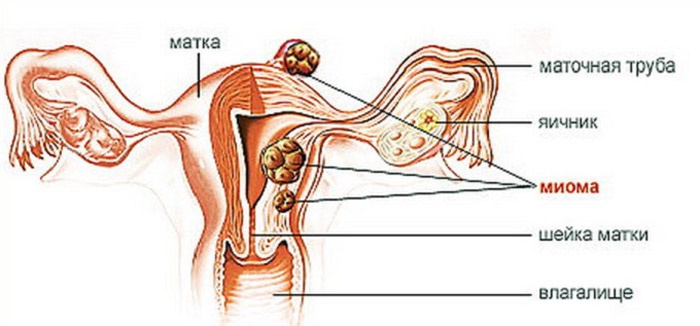
Myoma
Myoma is a benign tumor that develops with a hormonal disorder. Due to myomatous nodes, the area of the endometrium increases, so the uterus is enlarged, and during heavy periods, clots are released, the patient is worried about pain during urination or defecation. The peak of the disease occurs at 35-50 years, and is usually diagnosed in women of reproductive age..
Usually, myoma does not give pronounced symptoms and is detected by a medical examination. Vivid symptoms mean that the size of the fibroid is large, therefore surgical intervention is required. But there are some symptoms that should alert a woman:
- Long and plentiful periods.
- Large clots of blood with mucus.
- Pain in the lower back and lower abdomen.
- Dysfunction of the gastrointestinal tract or urinary tract.
Endometriosis
Large blood clots can cause endometriosis, when the endometrium lining the inner surface of the uterus grows too much, affecting the internal organs. The cause of dense endometriosis is caused by numerous abortions, iron deficiency, obesity, hormonal disorders, or a genetic predisposition. The symptoms of endometriosis are so diverse that sometimes even the most experienced gynecologists are misleading. However, there are pronounced symptoms:
- pain symptoms in the lumbar belt or lower abdomen;
- during menstruation, strong blood clots and menstrual irregularities;
- infertility;
- intoxication: vomiting, weakness, chills, sometimes fever.
Uterine anomaly
Abundant periods with blood clots occur if a woman has a congenital abnormality of the uterus. This disease occurs in 2% of women, and play a decisive role in whether they can have children. Sometimes a woman with such a pathology manages to conceive and give birth, but pregnancy and childbirth are complicated: miscarriages are often observed at different times. Abnormal structures of the uterus:
- two-horned;
- saddle-shaped;
- one-horned;
- with a partition;
- agenesis;
- full doubling.
Common saddle and two-horned uterus. In the first case, the part of the organ under the upper arch has not a convex, but a bottom pressed inward, in which partitions are formed. With this anomaly, it is possible to bear the fetus, but partitions usually become the causes of many problems. As for the two-horned organ, then there are 2 cavities in it, connecting in the center or around the neck.
Pelvic disease
Inflammatory processes in the pelvic organs of a woman include any combination of pelvic peritonitis, endometritis, tubo-ovarian abscess, or salpingitis. Typically, these diseases are sexually transmitted, but can also be formed by microorganisms of the vaginal microflora. Inflammatory processes are diagnosed on the basis of complaints and clinical examination. The treatment of diseases is carried out using conservative therapy, depending on the clinical form of the disease..
Coagulation Disorders
The system of hemocoagulation (blood coagulation) activates fibrinogen dissolved in the blood plasma and forms firbin blood clots in the blood vessels that stop any bleeding. Various diseases of blood vessels or blood lead to bleeding disorders, which are manifested in the form of causeless bruises, non-stop bleeding during injuries or during heavy periods with blood clots in women.
Imbalance in the hormonal balance in the body
Hormones are produced by the ovaries, pituitary, adrenal glands, pancreas and thyroid gland. The totality of all hormones is responsible for women’s health. If the body lacks any kind of hormones, then the following deviations begin:
- failure of the menstrual cycle, as well as blood clots and heavy discharge during menstruation;
- sudden weight loss or vice versa, overweight;
- digestion disorder;
- breast swelling;
- tumor development;
- prostration.
The causes of hormonal imbalance are many. For example, in adolescents, this is a temporary physiological process associated with the development of the body. And in women, hormonal storms occur after childbirth, after a delay in menstruation or after a miscarriage, during pregnancy, with the onset of menopause or during breastfeeding. Also, malnutrition, bad habits, or chronic fatigue easily become the cause of hormonal failure..
In which cases it is worth visiting a doctor?
If you are planning a pregnancy, then blood clots during menstruation should be cause for concern. The appearance of clots indicates the inability of the ovum to attach to the uterus. If during menstruation there were not only clots, but also aching pain in the lower abdomen – then you need to visit a gynecologist in any case: are you planning a pregnancy or not.
Treatment
Treatment of gynecological pathologies requires proper diagnosis. The examination includes MRI, pelvic ultrasound, laboratory and cytological studies. If the diagnosis does not show anything serious, the doctor will prescribe iron-containing drugs that will restore low hemoglobin from blood loss during menstruation. In other cases, either conservative treatment or surgery is prescribed, if the situation is especially running.