Content
- What causes a cyst in the head
- Types of Arachnoid Cyst
- What is the danger of retrocerebellar arachnoid cyst
- The main signs and symptoms of education
- Diagnostic Methods
- Treatment methods
- Forecasts and Implications
- Prevention
In most cases, the arachnoid cyst does not manifest itself. It is small and, as a rule, does not grow and does not prevent a person from living a normal life. In rare cases, a neoplasm makes itself felt when it provokes the appearance of unpleasant and dangerous symptoms for a person.
What causes a cyst in the head
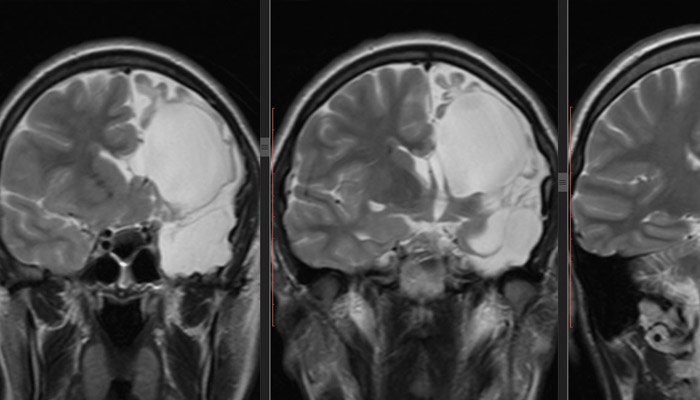
A benign spherical formation – a cyst in the brain – inside is filled with cerebrospinal fluid. The severity of symptoms depends on the size of the neoplasm, but it is found during an accidental medical examination or when diagnosing any other disease. The arachnoid cyst of the brain is asymptomatic in most cases. Vivid neurological symptoms are present in only 20% of patients. Factors affecting the appearance and growth of a cyst:
- any brain injury;
- growth within the cystic formation of fluid pressure;
- inflammatory process in the brain (infection, virus).
Types of Arachnoid Cyst
Leading specialists in the field of medicine today identify two types of neoplasms that differ in cause of occurrence. The first is the primary, which develops the baby in the womb. Secondary manifests itself in the process of the above pathologies. Also, a cyst can be simple, formed from cerebrospinal fluid, and complex, containing a variety of types of tissues. At the location of the neoplasm in the brain is divided into:
- left or right temporal lobe;
- the parietal or frontal part of the head;
- cerebellum;
- spinal canal;
- posterior cranial fossa;
- spine (perineural);
- lumbar.
Primary (congenital)
It can form due to inflammatory processes that developed during the prenatal period. The cause of the appearance of a neoplasm is sometimes a birth injury, a disease of meningitis in a newborn. Numerous violations of the fetal development due to smoking, taking medications, drinking alcohol by a pregnant woman are frequent. If the primary cyst progresses rapidly, then with severe symptoms it can be removed at any age of the child.
Secondary (acquired)
This type of arachnoid cyst of the brain develops after diseases, injuries, and surgical interventions. The occurrence can provoke a severe blow to the head, concussion after an accident, subarachnoid hemorrhage or mechanical damage. When a secondary cyst begins to form due to any pathology, its walls consist of scar tissue. If the cyst in the adult brain has developed for another reason, then its walls contain arachnoid tissue.
What is the danger of retrocerebellar arachnoid cyst
This type of neoplasm is located between the soft and hard shell of the brain. A risk factor is that a retrocerebellar arachnoid cyst can subsequently contribute to the death of cells, and this condition leads to the appearance of a malignant tumor. In children, neoplasm leads to developmental delay or hypermobility syndrome. In adults, a growing cyst increases pressure on the gray matter and brain tissue.
The main signs and symptoms of education
Signs of a cyst are manifested with its growth. Headaches begin, tinnitus disrupts the sensitivity of the skin. If the arachnoid cyst of the brain is not treated, then paralysis of the extremities may occur, epileptic seizures may appear, deafness may increase and vision will be lost. The symptomatology of the disease is characteristic of a specific area of the lesion..
In adults
Small bubbles with liquid contents in the tissues of the brain do not pose a threat to a person, and he easily lives with them all his life. Large formations of a progressive type have clear signs of pathology. It:
- loss of orientation;
- regular migraine;
- sleep loss
- violation of muscle tone;
- lameness;
- nausea, vomiting;
- twitching of limbs (involuntary);
- dizziness.
In children
When a cyst is formed in newborns as a result of inflammation, damage, or other pathology of the brain, then this is a ramolation formation, which manifests itself anywhere. If the baby has parasites, for example, tapeworm, then a parasitic cyst may develop. Neoplasms of the brain are a consequence of a violation of the circulation of interstitial fluid. Symptoms depend on the location and type of cyst, but there is no universal list of them. The following conditions may indicate a brain pathology in a child:
- pulsating fontanel;
- lethargy of limbs;
- disoriented gaze;
- belching after feeding.
Diagnostic Methods
The optimal diagnostic method of pathology is MRI of the brain. If there is a cyst in the final description of the results of tomography, it will be indicated: “arachnoid changes of cerebrospinal fluid character.” The location of the formation reveals the use of contrast agents. The main property of the neoplasm, in contrast to the tumor, is the ability to accumulate contrast. If necessary, laboratory tests, studies are carried out:
- blood for cholesterol;
- to detect infections;
- dopplerography of blood vessels;
- blood pressure measurement (reveals its jumps).
Treatment methods
The methods of treatment for the disease will depend on the results of the diagnosis. If the arachnoid cyst of the brain is small, then it does not pose a health hazard. The patient will be monitored by a doctor and periodically examined. During this period, it is important to eliminate the cause of the pathology and minimize the influence of negative factors. If the neoplasm grows rapidly, then drug therapy or surgery will be used..
Drug therapy
Medium-sized cysts can be eliminated with medication. The course of treatment is prescribed individually and is carried out under the supervision of a doctor until the patient’s condition improves. Names of drugs that can stop the growth of a neoplasm:
- absorbable adhesions: Longidaz, Caripatine;
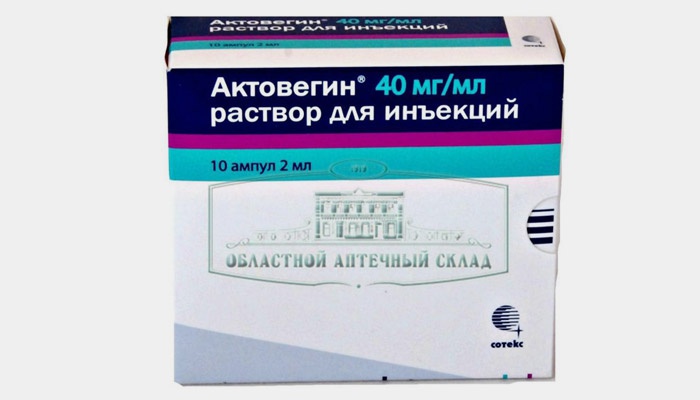
- activating metabolic processes in tissues: Actovegin, Gliatilin;
- immunomodulators: Viferon, Timogen;
- Antiviral: Pyrogenal, Amixin.
Folk remedies and herbs
With an asymptomatic cyst of the brain, it is possible to maintain the body with alternative recipes:
- Hemlock herb tincture. Eliminates headaches. The duration of treatment is 79 days. If necessary, the course is allowed to be repeated. You can prepare the tincture as follows: 100 g of seeds or chopped stems are poured with olive oil (0.5 l). For three weeks, the solution should be left in a dark place. After the oil is passed through cheesecloth several times. Tincture is taken through the nose 3 times / day, 2 drops.
- Infusion from the root of the Caucasian dioscorea. Favorably affects the brain: cleanses and dilates blood vessels. The course of administration is 2-3 months. The root (200 g) is crushed, the jar is filled, 700 ml of vodka are poured. In a cool place, the composition is infused for 5 days. After the infusion is merged, and another 700 ml of vodka is poured. After 5 days, both formulations are mixed, filtered and consumed in 2 tsp. three times / day before meals.
- Elixir made of yeast. Helps to reduce inflammation, normalize intracranial pressure. The course of treatment is three weeks. Yeast (1 tbsp) is mixed with dried elecampane grass (40 g) and three liters of boiled water. Insist 2 days, then take 4 times / day for half a glass.
Surgical intervention
If the brain cyst increases in size, then an operation to remove it will be prescribed. Modern medicine involves several types of surgical intervention:
- endoscopic method – the least traumatic when the contents are removed through punctures;
- Surgery bypass surgery is performed by introducing a drainage tube into the cyst cavity (high risk of infection);
- fenestration is performed by excision of the formation using a laser;
- puncture, which involves removing the capsule with an ultra-thin instrument (a high probability of a neurological complication);
- craniotomy is the most radical and effective operation, combined with increased trauma.
Forecasts and Implications
With the timely detection of brain cysts, the prognosis is favorable. The main risks associated with arachnoid formation are compression of the brain centers, after which disturbances in the body work. After removal of the cyst, speech, hearing or vision impairment is sometimes observed. If untimely diagnosis is possible, rupture of the cyst, hydrocephalus, death.
Prevention
Changing the size of an arachnoid cyst does not need to be perceived as an oncological disease, but preventive measures should be taken to maintain brain health. These include: compliance with physical activity, proper nutrition, rejection of bad habits. After 40 years, it is advisable for people after six months to visit a cardiologist and a neurologist for examination.
Similar articles
- Hydrocephalus of the brain – what is it. How to treat brain hydrocephalus in adults and children
- Brain tumor – symptoms in the early stages. The first manifestations and diagnosis of a brain tumor in children and adults
- Headache in forehead and eyes – what to do. Types of headache in the forehead and eyes and treatment